Automation has become a cornerstone of modern industry, driving efficiency, precision, and innovation across sectors like manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and more. At the heart of automation are electric motors, powering the machines and systems that streamline complex processes. Their ability to provide reliable, energy-efficient, and precise control has made them indispensable in the automation industry.
This blog explores the impact of electric motors on automation and highlights their applications in this transformative field.
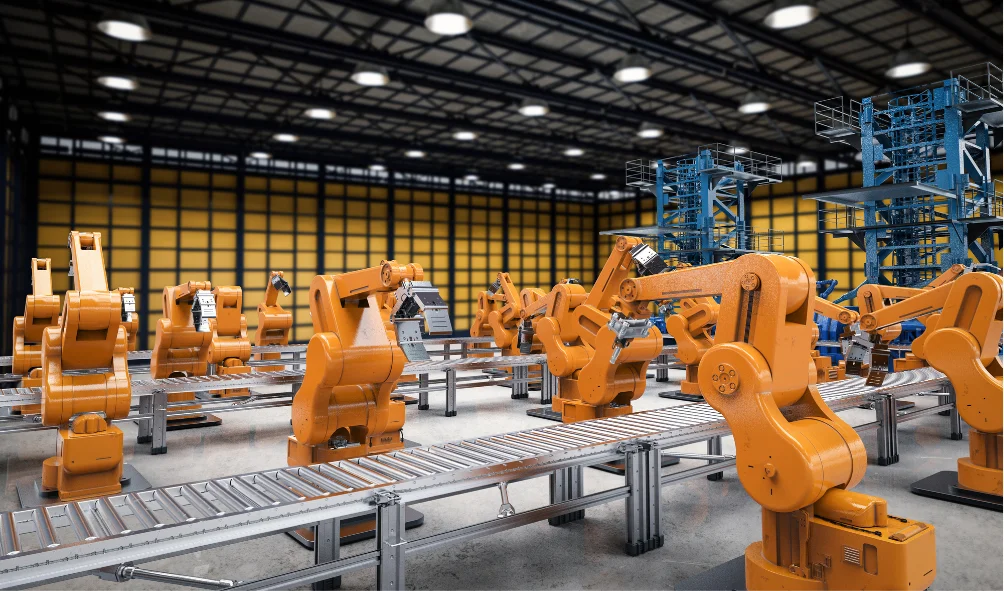

Impact of Electric Motors in the Automation Industry
1. Precision and Control
Automation relies on precise movements and operations. Electric motors enable:
- Accurate control of speed, position, and torque.
- Seamless integration with advanced control systems like PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition).
2. Energy Efficiency
Electric motors drive energy savings in automated systems by:
- Operating with high efficiency, reducing energy consumption.
- Supporting Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) that adjust motor speed based on real-time demand.
3. Reliability and Durability
Automated systems often require 24/7 operation. Modern electric motors are:
- Built for continuous use with minimal maintenance.
- Engineered to withstand demanding conditions in industrial environments.
4. Scalability and Versatility
Electric motors cater to a wide range of automation applications, from micro-motors in medical devices to large industrial motors for heavy machinery.
Applications of Electric Motors in the Automation Industry
1. Robotics
Electric motors are the backbone of robotic systems, powering:
- Robotic arms for assembly, welding, and painting.
- Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) used in logistics and material handling.
- High-speed pick-and-place robots in manufacturing.
2. Conveyor Systems
Motors drive conveyors used for:
- Transporting materials and goods in warehouses, factories, and distribution centers.
- Sorting and packaging processes in automated lines.
3. CNC Machines
Electric motors enable precision in Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines by:
- Controlling cutting tools and workpieces.
- Ensuring accuracy in machining, milling, and 3D printing.
4. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
AGVs use electric motors for:
- Navigation and movement within warehouses and factories.
- Efficient handling of materials without human intervention.
5. Actuators in Automated Systems
Motors power linear and rotary actuators that:
- Control valves, dampers, and other mechanical systems.
- Facilitate motion in automated assembly lines.
6. Smart Home Automation
In consumer applications, electric motors drive:
- Motorized blinds, smart locks, and automated curtains.
- HVAC systems for efficient heating, ventilation, and cooling.
Technological Advancements in Electric Motors for Automation
1. Servo Motors
Servo motors are integral to automation, offering:
- High precision in position and speed control.
- Fast response times for dynamic applications like robotics.
2. Stepper Motors
Popular in precision tasks, stepper motors:
- Provide incremental movements for tasks requiring fine adjustments.
- Are used in 3D printers, medical devices, and lab equipment.
3. Brushless DC Motors (BLDC)
BLDC motors deliver:
- High efficiency and low maintenance due to the absence of brushes.
- Silent operation, making them ideal for environments like healthcare.
4. IoT-Enabled Smart Motors
Smart motors with IoT capabilities support:
- Real-time monitoring and diagnostics.
- Predictive maintenance to prevent unexpected downtime.
- Integration with Industry 4.0 technologies for enhanced automation.
Challenges and Solutions
Challenges:
- Complexity of Integration: Incorporating electric motors into advanced automation systems can require sophisticated programming and control.
- Initial Costs: High-performance motors and smart motor systems may involve significant upfront investment.
Solutions:
- Modular Systems: Standardized motor modules simplify integration into automation frameworks.
- Lifecycle Cost Benefits: Energy savings and reduced maintenance costs make electric motors a cost-effective choice over time.
Benefits of Electric Motors in Automation
- Increased Efficiency: Motors enable faster and more efficient processes, reducing production times.
- Enhanced Precision: Automation driven by electric motors ensures consistent and accurate results.
- Reduced Energy Costs: High-efficiency motors lower operational expenses.
- Scalability: Motors can power systems of any scale, from small devices to large industrial setups.
Future Trends in Electric Motor Technology for Automation
1. Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Motors in automated systems are increasingly being paired with AI algorithms to:
- Optimize energy use.
- Adapt performance based on environmental data.
2. Adoption of Renewable Energy
Electric motors are compatible with renewable energy sources, enabling eco-friendly automation systems.
3. Miniaturization
The development of smaller, high-performance motors is expanding automation into fields like medical implants and nano-technology.
=
Conclusion
Electric motors are the lifeblood of automation, driving efficiency, precision, and scalability across industries. Their integration with smart technologies and renewable energy systems is shaping the future of automation, enabling sustainable and innovative solutions. As industries continue to automate, electric motors will remain a fundamental component of progress.
How do you envision the role of electric motors evolving in the automation industry? Share your thoughts below!